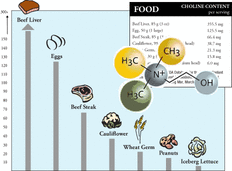
Choline is an important micronutrient for endurance athletes, pregnant and postmenopausal women. It is needed for neurotransmitter synthesis (acetylcholine), cell-membrane signaling (phospholipids), lipid transport (lipoproteins), and methyl-group metabolism (homocysteine reduction). It is important for brain and memory development in the fetus and appears to decrease the risk of the development of neural tube defects. Most common signs of choline deficiencies are fatty liver and hemorrhagic kidney necrosis.
Choline is a precursor to trimethylamine, which some individuals are not able to break down due to a genetic disorder called trimethylaminuria or certain types of microbial dysbiosis. These individuals have a strong fishy or otherwise unpleasant body odor that can occur even on a normal diet, not particularly high in choline and they need to dramatically reduce it. In this case, recommended intake is 30 to 40mg taken 3 to 5 times per day with food. The recommended adequate intake of choline for those not-suffering from TMAU is set at 425 milligrams (mg)/day for women and 550 mg/day for men.
