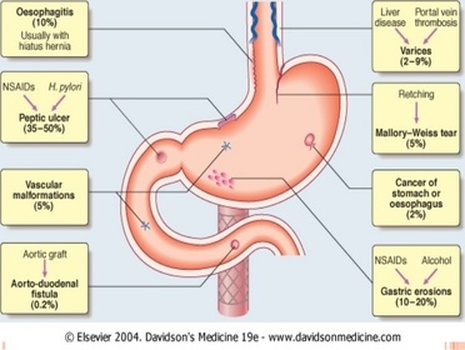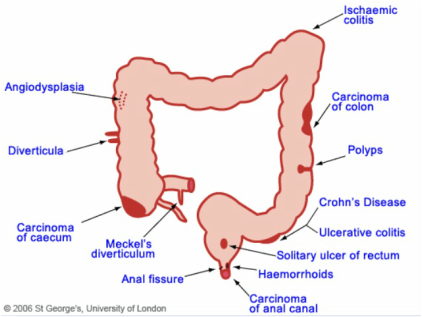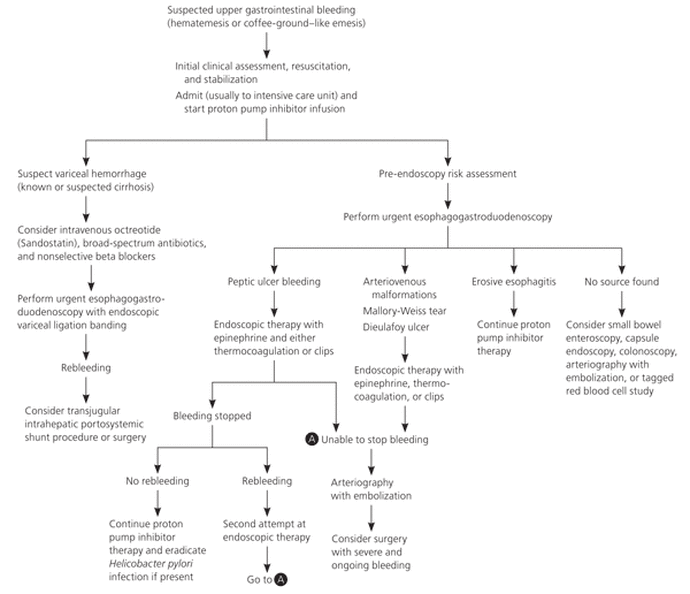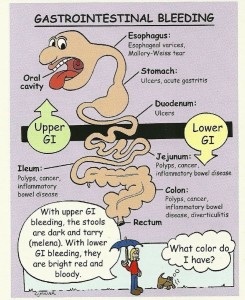
GI bleeding first appears as blood in vomit or stool, black or tarry stools. It can be suspected if the person experiences abdominal pain, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, anemia. GI bleeding can be diagnosed by lab tests and procedures such as endoscopic procedures: esophagogastroduedonoscopy (EGD), gastroscopy, endoscopic ultrasound, sigmoidoscopy, or colonoscopy. The causes of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding are classified into upper or lower, depending on their location in the GI tract. Treatment depends on the cause or location of the bleeding and includes:
- injecting medications/glues into the bleeding site (endoscopic injection, intravariceal cyanocrylate injection, angiographic embolization)
- "burning" (coagulating) the bleeding site and surrounding tissue with a heat probe, an electric current, or a laser (endoscopic thermal probe, argon plasma coagulation and radiofrequency ablation),
- closing affected blood vessels with a band or clip