1st Generation Web, a.k.a internet before the bursting of the dot-com bubble, was a dial-up, 50K bandwidth, built around fixed content, with static pages and framesets providing one-way web of information.
Web 2.0 – first used in January 1999 by Darcy DiNucci and popularized in 2004is is "an average 1 megabit of bandwidth" – according to Netflix’ Reed Hastings.
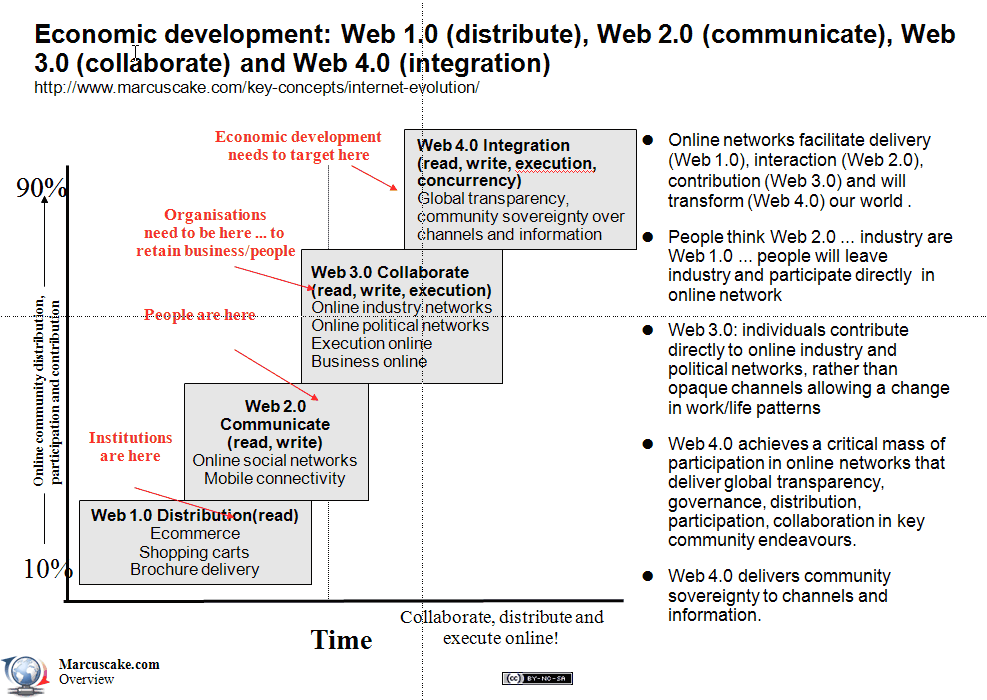
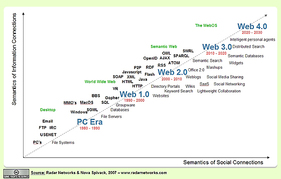
- Web 1.0 is “read-only”
- Web 2.0 is “read-write” (blogs, RSS feeds, tagging, shopping carts)
- Web 3.0 is “read-write-execute”: small apps with data in the cloud – google vision; or a true communal media – yahoo vision. It is semantic and executing.
- Web 4.0 is "read-write-execution-concurrency", open, symbiotic and fully executing, it will form when all of the above come together to form the learning self-aware Web, the era of artificial intelligence.
Web 1.0 Web 2.0
DoubleClick---------->Google AdSense
Ofoto------------------->Flickr
Akamai----------------->BitTorrent
mp3.com-------------->Napster
Britannica Online-->Wikipedia
Personal Websites-->blogging
evite------------>upcoming.org and EVDB
Domain Name Speculation-->Search Engine Optimization
page views------>cost per click
screen scraping--->web services
publishing--------------->participation
content management systems-->wikis
directories (taxonomy)--->tagging ("folksonomy")
stickiness--------->syndication

Business models for health care are also evolving - from solution shops to facilitated networks, transforming the organization of health care delivery.
So, what is Health 4.0? Here is Jen McCabe's opinion:
- Health 1.0 = content
- Health 2.0 = content + community
- Health 3.0 = content + community + consumer-centric commerce
- Health 4.0 = content + community + working commerce models + coherence
Blog of a non-for profit hospital chain CHW gives the following definitions:
- Health 1.0 Disenfranchised patients, a “Dr. Knows Best” approach.
- Health 2.0 The empowered consumer
- Health 3.0. Personal responsibility becomes part of the social contract we all have with one another. Not only will consumers be given the tools and information they need to make better choices — they’ll be expected to do so. And there will be consequences for not doing so.
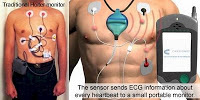
But consumer owned healthcare’ isn’t quite here yet, even though number of US Health 2.0 consumers is at 60 million. 10 million adults use their cell phones and PDA/smartphones to look up health and medical information, and “a growing number of patients are rating prescription drugs and treatments on sites likeiGuard.org, DailyStrength.org, PatientsLikeMe, and WebMD.” See the top health web apps, the trends to watch in health 2.0, the latest industry stats and Health 2.0 updates by ReadWriteWeb.
Long Live Health 2.0! Welcome first concepts of Health 3.0! And let’s start planning generation 4.






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
