Just one example of how this could be leveraged in Healthcare.

AI can predict heart attacks and strokes more accurately than a doctor - if there are good quality medical records. AI is better in analyzing visual information - if there are tenths of thousands of good quality images annotated for thousands of patients. But in most cases data we need for predicting outcomes is either too expensive to prepare or impossible to get - as it remains in the brains of individuals. And cages accurately monitoring food intake, activities and symptoms so far work only for mice.
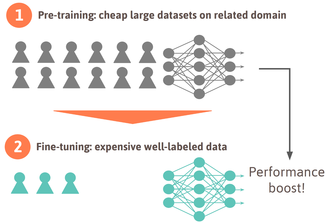
In the world of humans, efficiency of medical research could be improved if cheap large datasets focusing on particular medical questions could be easily collected. If clinical trials were more engaging and convenient, generating outcomes clinically meaningful to participants; if the participants could properly design studies by themselves, guided by Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) platform and their own devices (BYOD model), we could collect enough data to get to the next level.
Scuffham PA, Nikles J, Mitchell GK, Yelland MJ, Vine N, Poulos CJ, Pillans PI, Bashford G, Del Mar C, Schluter PJ, Glasziou P. Using N-of-1 trials to improve patient management and save costs. Journal of general internal medicine. 2010 Sep 1;25(9):906-13.
Lillie EO, Patay B, Diamant J, Issell B, Topol EJ, Schork NJ. The n-of-1 clinical trial: the ultimate strategy for individualizing medicine?. Personalized medicine. 2011 Mar;8(2):161-73.
Sackett DL. Clinician-trialist rounds: 4. Why not do an N-of-1 RCT?.
Li J, Tian J, Ma B, Yang K. N-of-1 trials in China. Complementary therapies in medicine. 2013 Jun 30;21(3):190-4.
Nyman SR, Goodwin K, Kwasnicka D, Callaway A. Increasing walking among older people: A test of behaviour change techniques using factorial randomised N-of-1 trials. Psychology & health. 2016 Mar 3;31(3):313-30.
Federman DG, Shelling ML, Kirsner RS. N-of-1 trials: not just for academics. Journal of general internal medicine. 2011 Feb 1;26(2):115-.
Duan N, Kravitz RL, Schmid CH. Single-patient (n-of-1) trials: a pragmatic clinical decision methodology for patient-centered comparative effectiveness research. Journal of clinical epidemiology. 2013 Aug 31;66(8):S21-8.
Joy TR, Monjed A, Zou GY, Hegele RA, McDonald CG, Mahon JL. N-of-1 (single-patient) trials for statin-related myalgia. Annals of internal medicine. 2014 Mar 4;160(5):301-10.
Shaffer JA, Falzon L, Cheung K, Davidson KW. N-of-1 randomized trials for psychological and health behavior outcomes: a systematic review protocol. Systematic reviews. 2015 Jun 17;4(1):87.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
