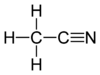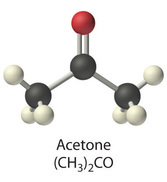
Acetone occurs naturally in plants, trees, forest fires, vehicle exhaust and as a breakdown product of animal fat metabolism. It may be normally present in very small quantities in urine and blood; larger amounts may be found in the urine and blood of diabetics. Larger concentrations of acetone in breath are also associated with fasting and sinusitis.