increased desire to eat. Could be caused by physical exertion or dieting and alleviated after eating. Other reasons could be premenstrual syndrome, stress, anxieties, reaction to medications (corticosteroids, cyproheptadine, tricyclic antidepressants, etc). Significantly increased appetite over a prolonged period, especially if it is accompanied by additional symptoms, could be a symptom of a serious illness, such as diabetes or hyperthyroidism.
Comments
 Rapid, shallow breathing, also called tachypnea or tachypnoea (Greek for "rapid breathing") is the process of taking more than normal air into and expelling it from the lungs. Hyperventilation is a condition in which a person suddenly starts to breathe very quickly upsetting the balance between breathing in oxygen and breathing out carbon dioxide. For adult humans at rest, tachypnea is indicated by a ventilatory rate greater than 20 breaths per minute. Average respiratory rates: Newborns: 44 breaths per minute Infants: 20–40 breaths per minute (over 50 if sick) Preschool children: 20–30 breaths per minute (over 40 if sick) Older children (5-8): 16–25 breaths per minute (over 30 if sick) Healthy Adults: 12–18 breaths per minute (up to 70 if stressed or exercising) Adults with Asthma: 24-30 breaths per minute (12-15 l/min) Adults with Heart Disease : 28-32 breaths per minute Adults with Diabetes: 20-40 breaths per minute 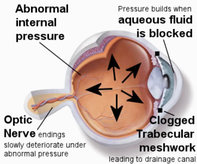 Also called Ocular hypertension or increased intraocular pressure is when the pressure inside the eye (intraocular pressure or IOP) is higher than normal. If it stays high or continues to increase, it exerts a force within the eye's interior that can damage the eye's delicate optic nerve, causing glaucoma. Intraocular pressure is caused by the fluid inside the eye (aqueous humour) mainly determined by the coupling of its production and the drainage. Normal eye pressure ranges from 10 to 21 mm.  Increased heart rate or pulse is higher number of times a person's heart beats per minute. A normal heart rate depends on the individual, age, body size, heart conditions, whether the person is sitting or moving, medication use and even air temperature. The usual range for resting heart rate is anywhere between 60 and 90 beats per minute. Generally, a lower heart rate at rest implies more efficient heart function and better cardiovascular fitness. For example, a well-trained athlete might have a normal resting heart rate closer to 40 beats a minute. Above 90 is considered high. Over 100 beats per minute is called tachycardia. This can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, or a fluttering in the chest. 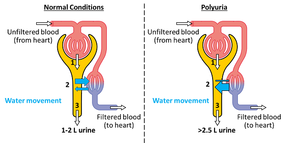 The need to urinate more than one usually does. Dysuria is any discomfort associated with urination. Abnormally frequent urination (e.g., once every hour or two) is termed urinary frequency - an abrupt, strong, often overwhelming, need to urinate. Medical term for excessive passing of urine (increase in total volume) is Polyuria. An excessive volume of urination for an adult is more than 2.5 liters of urine per day. Normally, adults pass between 3 cups (700 milliliters) and 3 quarts (3 liters). of However, this can vary depending on the liquid intake. 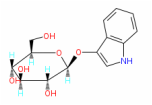 Indican is a colorless glycoside, soluble in water, naturally occurring in Indigofera plants. In the body it is produced by bacteria - by sulfonation of indole (absorbed by the colon and transported to the liver), a compound with intense fecal odor, degradation product of tryptophan which is derived from protein foods. IUPAC Name: 1H-indol-3-yl hydrogen sulfate | CAS Registry Number: 487-94-5 Synonyms: Indoxyl sulfate, 3-Indoxyl sulfate, Indoxylsulfuric acid, INDICAN, 3-Indoxylsulfuric acid, Indican (metabolic indican), 3-SULFOOXY-1H-INDOLE, CID10258, Indican (metabolic indolyl sulfate), 2642-37-7 (mono-potassium salt), 1H-Indol-3-ol, hydrogen sulfate (ester), IOS, 1336-79-4, 487-94-5 A high excretion of indican in the urine, mostly combined with a low urinary tryptophan, is a symptom of tryptophan (protein) malabsorption in the small intestine. It also indicates an overgrowth of opportunistic or pathogenic bacteria or yeast in the bowel and more serious conditions like Hartnup's disease, blue diaper syndrome, intestinal toxemia, or peritonitis. Low indican excretion could indicate the presence of steatorrhoea (reduced absorption of fat) especially if it rises to above normal on pancreatic enzyme therapy. The urine indican's (or Obermeyer) test quantifies indican in the urine based on its decomposition and subsequent oxidation to indigo blue. Check MeBO-Biolab studies (NCT02692495) for more. 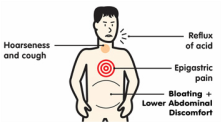 Disorder of digestive function, a condition of impaired digestion characterized by vague discomfort in the upper abdomen (nausea) or chest (heartburn), usually soon after meals. Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia or upset stomach, is the condition, while heartburn, fullness, nausea, bloating, excess gas, pain, burning and gnawing are symptoms. 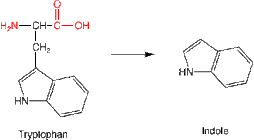 organic compound, a bacterial degradation product of amino acid tryptophan that occurs naturally in human feces and coal tar. In its pure form, indole smells like moth balls, possessing the same heavy, sweet, tar-like pungency. At very low concentrations, however, it has a pleasant, flowery smell. Natural jasmine oil, used in the perfume industry, contains around 2.5% of indole. Orange blossom and Neroli contain even more indoles than jasmine. Fragrances like Chanel Cristalle, By Kilian Love & Tears and L’Artisan Parfumeur La Chasse Aux Papillons rely on a delicate touch of indoles to give radiance and bloom to their floral accords.In trace amounts, Indoles are also used to create chocolate, coffee and various fruity accords in flavors, including food. Indole is an important biomarker in biological and clinical specimens. It can be detected in human breath, feces, saliva and urine. The normal smell of human feces is largely due to this compound. Indole is an example of a microbe-generated signal substance that has positive effects on our health and the health of the microbiome. Normal-smelling feces may be an underestimated health indicator. In the liver indole is sulfonated to indican (3-indolesulfonic acid) and its levels could be also indirectly measured by indicans test. See MeBO-Biolab studies (NCT02692495) for more. 
non-metallic trace element, needed for the normal metabolism of cells. in particular for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. It is used as mild antiseptic. Deficiency may case an enlarged thyroid gland (goitre), dry skin, hair loss, fatigue and slowed reflexes. Anecdotal evidence exists that long term Iodine deficiency may cause breast cancer. Large doses of iodine (radioiodine therapy and supplement overdose) are dry mouth, taste change, iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis. More than adequate or excessive iodine intake may lead to hypothyroidism and autoimmune thyroiditis. Main sources are seaweed, iodized salt, seafood, dairy.
|
Categories
All
|