Examples: problem solving, socializing, strength exercise, abdominal exercises, sexual activity
 something done as an action or a movement, for pleasure, as work (measurable amount of work performed to convert inputs into outputs), or for any other particular purpose. Examples: problem solving, socializing, strength exercise, abdominal exercises, sexual activity
Comments
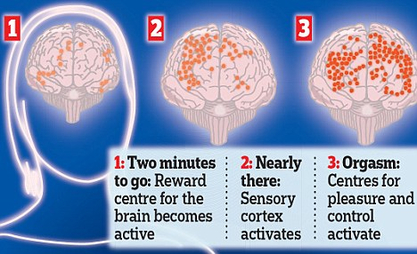 A type of spontaneous orgasm during sleep Ejaculation during sleep for a male, or lubrication of the vagina for a female. In 1953, Alfred Kinsey found that nearly 40% of the 5,628 women he interviewed experienced at least one nocturnal orgasm or "wet dream," by the time they were forty-five years old. A smaller study published in the Journal of Sex Research in 1986 found that 85% of the women who had experienced nocturnal orgasms had done so by the age of twenty-one or earlier. Women who have orgasms during sleep usually have them several times a year. Dr. Kinsey and his colleagues defined female nocturnal orgasm as sexual arousal during sleep that awakens one to perceive the experience of orgasm. Similar studies find that a much higher percentage of boys and men experience wet dreams. Relatively small studies conducted in the 50s found that nocturnal orgasm was reported by about 40% of women with the diagnosis of a neurosis or psychosis, and as opposed to only 6-8% of control women. Studies conducted in the 80s found that the incidence of nocturnal orgasms in healthy women is much higher and is associated with positive attitude to sex, knowledge about nocturnal orgasms and sexual liberalism. Later studies concluded that it was more about “erotic responsiveness" than other factors.  an irresistible urge to perform certain meaningless actions persistently and repeatedly in order to alleviate obsessive fears or intrusive thoughts, in an attempt to make obsessions (frequent upsetting thoughts) go away. For example, if people are obsessed with germs or dirt, they may develop a compulsion to wash their hands over and over again. Other common rituals are a need to repeatedly check things, touch things (especially in a particular sequence), or count things. Healthy people also have rituals, such as checking to see if the stove is off several times before leaving the house. The difference is that people with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) perform their rituals even though doing so interferes with daily life and they find the repetition distressing.  Activity involving mental or physical effort to overcome obstacles and achieve a purpose or result. Calories burned range from 1.3 METs per Hr when reading (One MET - metabolic equivalent is defined as 1 kcal/kg/hour and is roughly equivalent to the energy cost of sitting quietly) to 1.8 METs/Hr when taking notes in class, 2.0 METs per hour when working on computer, 3.5 METs/hr when mopping floors, 6.5-8.8 when vigorously shoveling and 9.0 when carrying heavy loads. Examples of most intellectually demanding jobs are air traffic controlling, cryptography, accurate simultaneous interpretation, software engineering, design of complex chip/devices, neurosurgery, mathematics and physics. Music is the most intellectually demanding artform, and motocross is one of the most mentally demanding sports.  being in a position in which one's weight is supported by one's buttocks rather than one's feet when back is upright, especially when engaged in a particular activity. 1 Metabolic Equivalent of Task (MET), a physiological measure expressing the energy cost of physical activities, is defined as the rate of energy produced per unit surface area of an average person seated at rest. Here are sample METs per activities involving sitting: Sitting, playing with animals. light, only active periods 2.5 Sitting quietly, smoking. listening to music (not talking or reading), watching a movie in a theater 1.0 Sitting and reading 1.3 Sitting and eating 1.5 Sitting-arts and crafts, light effort 1.5 Sitting-arts and crafts, moderate effort 2.0 Sitting at a sporting event, spectator 1.5 Sitting while taking medication 1.0 Sitting while having hair or nails done by someone else 1.0  Process of interacting with other individuals and groups to exchange, compete, cooperate, conform, conflict or coerce. Social exchange is exchange of material goods and immaterial benefits.such as moral support, performed in the expectation of getting a reward in return. Competition is a contest for territory, a niche, resources, goods, mates, prestige, recognition, awards, social status, leadership. Cooperation works better when there are limited resources because individuals think more and try harder. Conformity is a behavior that matches a groups behavior, socially accepted conventions or standards - people frequently conform to avoid being different, but without conformity there would be no social culture. Conflict could be beneficial as it could promote cooperation and unity within opposing groups cause a needed change, and draw attention to social inequalities. Coercion is the opposite of social exchange.  the ability to make considered decisions or come to sensible conclusions by properly evaluating and placing the correct values on factors in a problem, such as the appropriateness and Importance of carrying particular actions. Situational Judgment Tests (SJT’s) are a type of psychological, aptitude tests assessing how one approaches situations encountered in the workplace. The test is usually delivered by presenting the test-taker with realistic, hypothetical scenarios and asking the individual to identify the most and the least effective responses. Situational judgment tests tend to determine behavioral tendencies, assessing how an individual will behave in a certain situation. 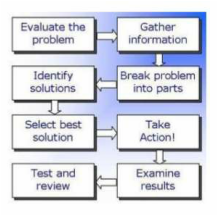 Finding solutions to difficult or complex issues using higher mental functions of the brain, creative thinking and strategies. Steps to solve a problem include Identifying and Defining the problem, Examining the options, Acting on plan, and Looking at the consequences. Techniques include TRIZ (based on logic and data, not intuition, focusing on the "contradictions"), Brainstorming (generating a large number of ideas in a group), Synectics (focusing on emotional and irrational components of creative behavior vs intellectual ones), Heuristic methods (based on finding similar problems and solutions, generalization, pattern recognition), and Mind mapping - an effective visual tool for structuring thoughts, organizing ideas in a form of decision trees. Problem solving is one of fundamental processes of cognition - the process of thinking, gaining knowledge, and using that knowledge. As a higher-layer cognitive process, problem solving interacts with abstraction, searching, learning, decision making, inference, analysis, and synthesis on the basis of internal knowledge representation. |
Categories
All
|