
Examples of electronics are wearable technologies, cell phones, computers, television sets, washing machines or circuits comprising them.
 Devices that operate using many small electrical parts where circulating electric current can flow, thus accomplishing their purpose electronically. Examples of electronics are wearable technologies, cell phones, computers, television sets, washing machines or circuits comprising them.
Comments
 Elixa probiotic contains the following 12 species of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus (strength: 500 billion CFUs):
anecdotal evidence exists that Elixa is increasing populations of Lactobacilli in the gut and decreases Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio that has been directly related to weight loss (elevated in obese subjects).  an injectable blood thinner (anticoagulant) used to treat and prevent blood clots especially after major surgeries (i.e., hip or knee replacement, abdominal surgery) or in very ill patients with limited mobility, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and for prevention of ischemic complications of unstable angina and myocardial infarction. Enoxaparin is a low molecular weight heparin with molecular formula C26H42N2O37S5. It is primarily metabolized in the liver by desulfation and/or depolymerization to smaller molecules. Brand names: Lovenox, Clexane, Lovenox HP, Clexane Forte Enoxaparin is given as an injection under skin in different areas of your body, usually in the fatty layer on the abdomen (the "stomach" area). Using the belly button as a reference point, one can inject him/herself anywhere from one inch above and one inch below the belly button. Injection can also be given in the thigh or fatty layer of the upper arm but preferably the abdomen or thigh. Recommended dose of Enoxaparin depends on the body weight, health condition, and other factors such as kidney function. For instance, if taking Enoxaparin to prevent blood clots after a heart attack, the dose is often 1 milligram for every 2.2 pounds of body weight every 12 hours for two to eight days. In patients undergoing abdominal surgery who are at risk for thromboembolic complications, the recommended dose of Enoxaparin Sodium Injection is 40 mg once a day administered by SC injection with the initial dose given 2 hours prior to surgery. The usual duration of administration is 7 to 10 days, up to 3 weeks after hip replacement surgery.  A combination of sacubitril and valsartan (ARB) used for heart failure. Sacubitrilat blocks the activity of enzyme neprilysin responsible for the degradation of blood pressure-lowering peptides that work mainly by reducing blood volume, relaxing blood vessels, decreasing sodium and fluid in the body.  biological molecules, mainly proteins, that catalyze (accelerate, increase the rates of) chemical reactions. Metabolic enzymes assist in a wide range of basic bodily processes, from breathing to thinking. One example of an enzyme is cytochrome, which aids the respiratory system by catalyzing the combination of oxygen with hydrogen within the cells. Cytochrome b is a part of complex III that helps to create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy source in mitochondria. Mutations in the MT-CYB (mitochondrially encoded cytochrome b) gene can cause muscle weakness (myopathy) and pain, especially during exercise (exercise intolerance). More severely affected individuals can have problems with other body systems, including the liver, kidneys, heart, and brain. Other enzymes are involved in digestion. Some of them come from raw foods and include proteases, digesting proteins; lipases, digesting lipids or fats; and amylases, helping to digest carbohydrates. Human digestive glands also secrete enzymes that break down nutrients - like amylase in the saliva and pepsin helping to digest protein in the stomach. 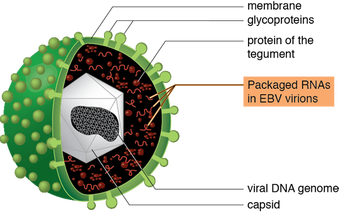 Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), also known as human herpesvirus 4, is a member of the herpes virus family. It is one of the most common human viruses. Most people get infected with EBV at some point in their lives. 80 - 90% of the adult population have been infected by the virus. EBV spreads most commonly through bodily fluids, primarily saliva. EBV can cause infectious mononucleosis (mono), and other illnesses. Like all herpesviruses, the Epstein-Barr virus is relatively large and complex. The virus's structure consists of an envelope, spikes, a core, a capsid and a tegument. All these structures aid in making the virus successful in the infection process and as a means of avoiding detection from our body's immune system. Most common symptoms of infection are extreme fatigue, fever, rash, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. 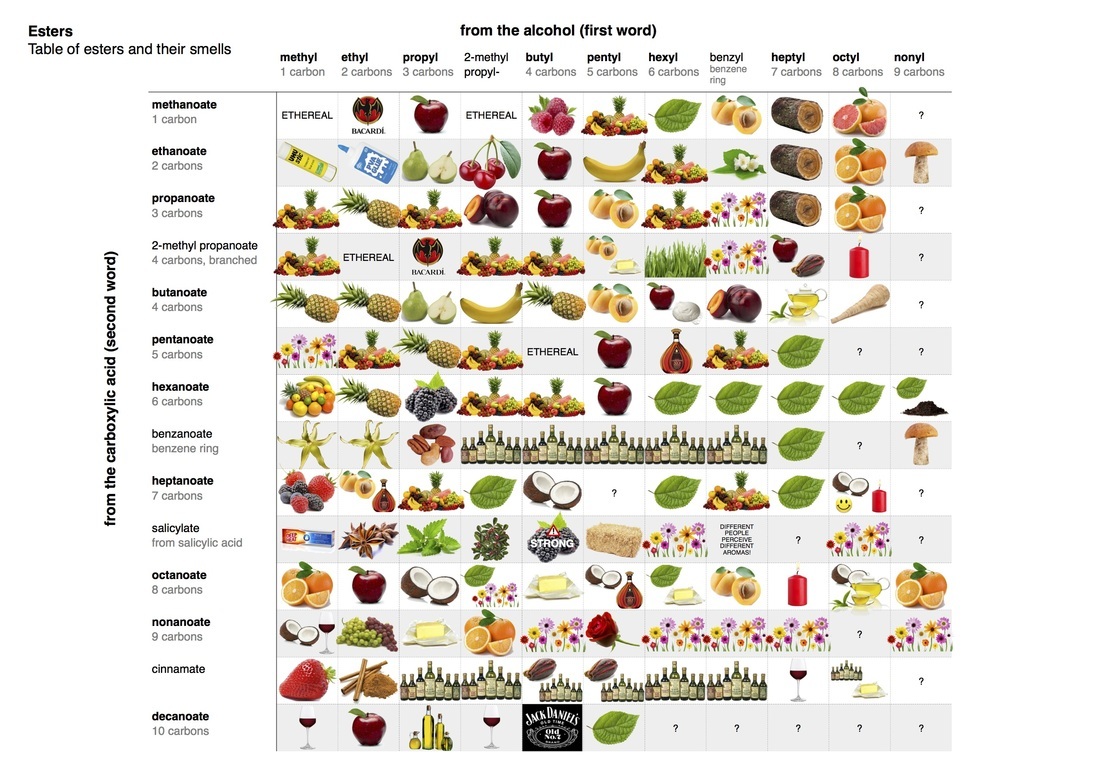 organic compounds made by replacing the hydrogen of an acid by an alkyl or other organic group. Many naturally occurring fats and essential oils are esters of fatty acids. Analysis of esters in urine, breath and other human fluids could aid in medical diagnostics. For example, carnitine and glycine esters in urine are associated with organic acidopathies, while certain esters in breath could indicate exposure to phthalates. 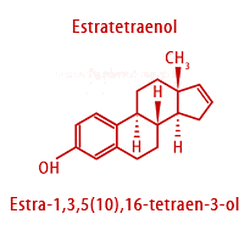 Estratetraenol, also known as estra-1,3,5(10),16-tetraen-3-ol, is a hormon-like endogenous steroid secreted by women (urine, sweat) that has been described as having pheromone-like activities. Its effects are smaller than those of androstadienone but go in the same direction - it makes women to appear more feminine and enhances men's arousal. Estratetraenol is synthesized from androstadienone by aromatase likely in the ovaries, and is related to the estrogen sex hormones, yet has no known estrogenic effects. 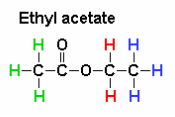 organic compound, ester of ethanol and acetic acid, carboxylic ester. It is produced by Acetobacter, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Baker's yeast) & other microbes, by Anthemis nobilis (Roman chamomile) and Rubus species (raspberries, blackberries). It is used as a plastics solvent and in flavorings, artificial fruit essences, confectionery and perfumes. It evaporates at a fast rate, leaving but the scent of the perfume on the skin. Ethyl acetate is also used as a solvent in the manufacture of modified hop extract and decaffeinated tea or coffee, for color inks to mark fruit or vegetables and as insecticide (asphyxiant) in the field of entomology. Ethyl acetate contributes to the notorious “nail polish remover” scent in wine and human body odor. It is also responsible for apple-like, banana-like, raspberry-like and strawberry aromas. Ethyl acetate is also found in cereal crops, radishes, fruit juices, beer,and other spirits. Short-term exposure to high levels of ethyl acetate results first in irritation of the eyes, nose and throat, followed by headache, nausea, vomiting, sleepiness, and unconsciousness. High concentrations can cause CNS depression and congestion of the liver and kidneys. Very high levels may cause a stupor but it is relatively non-toxic. Chronic poisoning has been described as producing anemia, leucocytosis (transient increase in the white blood cell count), and, clouding of the eye, damage to the lungs and heart and kidney and liver problems, cloudy swelling, and fatty degeneration. Athletes exposed to relatively lower levels of Ethyl acetate in facilities where they exercise experience wheezing coughing, rhinitis, or shortness of breath. Ethyl acetate has been shown to exhibit anti-arthritic, anti-mycotic, anti-nociceptive, hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory functions (PMID 12673020 , 12781815 , 21340514 , 17507320 ,20363280). Ethyl acetate belongs to the family of Carboxylic Acid Esters. These are carboxylic acid derivatives in which the carbo atom from the carbonyl group is atached to an alkyl or oaryl moiety through an oxygen atom (forming an ester group). Ethyl acetate can be found in human biofluids such as feces, saliva and urine. It is present in small amounts in healthy children and adults. Abnormal concentrations can be found in Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), Celiac disease and breast cancer.  Burning, throbbing, aching, stabbing sensation or discomfort in or around the eye. Can be caused by illness (glaucoma, optic neuritis, corneal infection, inflammation of the eyelid, conjunctivitis) or injury, abrasion and foreign body. Common causes of pain behind one eye accompanied by pain on the same side of the head (e.g., temple) is migraine headache. Sinusitis (Infection in one of the sinus cavities), can also create pressure behind the eyes, causing eye pain on one or both sides. |
Categories
All
|