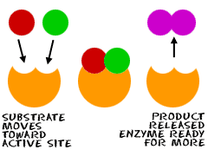
Metabolic enzymes assist in a wide range of basic bodily processes, from breathing to thinking. One example of an enzyme is cytochrome, which aids the respiratory system by catalyzing the combination of oxygen with hydrogen within the cells. Cytochrome b is a part of complex III that helps to create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy source in mitochondria. Mutations in the MT-CYB (mitochondrially encoded cytochrome b) gene can cause muscle weakness (myopathy) and pain, especially during exercise (exercise intolerance). More severely affected individuals can have problems with other body systems, including the liver, kidneys, heart, and brain.
Other enzymes are involved in digestion. Some of them come from raw foods and include proteases, digesting proteins; lipases, digesting lipids or fats; and amylases, helping to digest carbohydrates. Human digestive glands also secrete enzymes that break down nutrients - like amylase in the saliva and pepsin helping to digest protein in the stomach.
