
 Bacillus coagulans GBI-30, 6086 (GanedenBC30) is a spore-forming probiotic strain that is resistant to extreme temperatures and survives in the gut environment. It is added to many foods, beverages and supplements, functional foods, nutriceuticals, medical food, animal health and personal care products. It is claimed to help support digestive and immune health. Expected concentration of BC30 in food and drinks is 100 million to 2 billion CFU per serving.
Comments
 Gaseous substances in (or released from) the stomach or intestines in the digestive tract. Over 99% of the volume consists of nitrogen (N2), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen (H2) and methane (CH4), that are byproducts of the digestive processes, result of swallowed air or diffusion from blood and bacterial fermentation.Odor is determined by over 3000 different compounds comprising less than 1% of the volume. Metabolites include volatile sulfur compounds, indole, skatole, ammonia, and short chain fatty acids. Excess intestinal gas in the stomach or upper intestine usually results in excess burping or belching. Excess intestinal gas in the lower intestine may result in increased gas being expulsed through the rectum Excess gas remaining in either location can cause cramping or pain, often without an obvious pattern. The list of euphemisms for gas passing is very large (300+ in English) and includes expressions such as passing wind, flatulence, flatus, fart, air, and toot.  a cooking appliance which uses natural gas, propane, butane, liquefied petroleum gas or other flammable gas as a fuel source. Often preferred by professional chefs and enthusiastic cooks, gas stoves are known to deliver accurate cooking temperatures and do not heat up the kitchen to unbearable levels while in operation. Still they present the potential risk of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning, if are not properly installed, maintained and operated. According to a study published in Environmental Health Perspectives in 2013 gas stoves could also give off unhealthy levels of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and formaldehyde. Emissions of CO and formaldehyde were generally low. But emissions of NO2 may surpass the acceptable limits for outdoor air established by the Environmental Protection Agency. 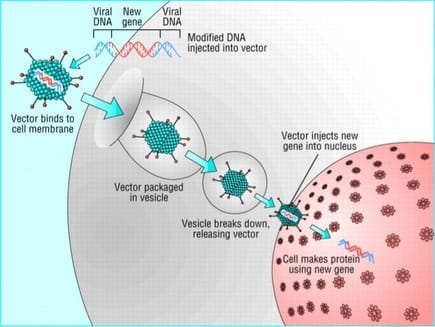 experimental therapeutic technique that manipulates genes to treat or prevent disease. The procedure assumes the transplantation of working genes into cells in place of missing or defective ones, and allows rescue of normal functions or the addition of new functions to cells to combat diseases. DNAi is inserted, deleted or replaced using "molecular scissors" - engineered nucleases creating site-specific double-strand breaks at desired locations in the genome. These breaks are further edited and repaired through nonhomologous end-joining or homologous recombination. There are currently four families of engineered nucleases being used: meganucleases, zinc finger nucleases, transcription activator-like effector-based nucleases, and the CRISPR-Cas system. 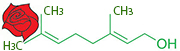 acyclic monoterpene-alcohol with a sweet rose-like scent. It's slightly ethereal and ozonic, even somewhat salty like sushi. It's a main chemical of rose oil, palmarosa oil, and citronella oil. It is naturally present in bergamot, carrot, coriander, lavender, lemon, lime, nutmeg, orange, rose, blueberry and blackberry. In acidic environments, it converts into alpha-terpineol that smells of lilac. Geraniol blends well with other flavors and is also a "floraliser“ enhancing, for example, green freshness of a rose. It is used in flavors such as peach, raspberry, grapefruit, red apple, plum, lime, orange, lemon, watermelon, pineapple, and blueberry. It is an active ingredient in Deo perfume candy and Otoko Kaoru chewing gums, hundreds of perfumes designed for men and women, lotions, shampoos, hairsprays, cigarettes, mosquito repellents and soaps. 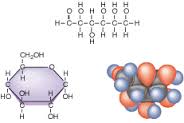 A simple monosaccharide (sugar) with a molecular formula of C6H12O6. Glucose has several forms. One form is D-glucose, also known as dextrose. The "D" refers to the arrangement of alcohol, or OH, groups on the carbon skeleton of the sugar. L-Glucose could be a low-calorie sweetener, but it does not occur in nature and is too costly to produce. Another form of glucose is beta-D-glucopyranose. As in straight chain D-glucose, the "D" refers to the arrangement of alcohol groups on the carbon skeleton. alpha-D-glucopyranose differs from beta- by the orientation of a single alcohol group around the cyclic carbon backbone. Alpha-D-glucopyranose can be found in solution, or combined with other molecules of sugar. Digestible starch is made of many hundreds of linked alpha-D-glucopyranose units.  proteins that remain when starch is removed from cereal grains, giving cohesiveness, viscosity and elastic texture to dough. Gluten proteins consist of the soluble gliadins (α, γ, and ω) and the insoluble glutenins. Each gluten protein type consists or two or three different structural domains; one of them contains unique repetitive sequences rich in glutamine and proline. Gluten proteins are found in grains like wheat, barley, and rye, commonly in foods like bread, baked goods, crackers, pasta, cereals. Surprising foods that may contain gluten includes caramels, licorice, soy sauce, salad dressings. For people with celiac disease (1% of population), gluten is toxic even at concentrations as little as 50 mg per day - or one fresh breadcrumb. For those with non-celiac gluten intolerance (common in allergic patients), slightly higher levels can be consumed. Common symptoms of Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) are mental fatigue ("brain fog"), lack of energy or lethargy, gas, bloating, abdominal pain or cramps, diarrhea and even constipation. At this time it is unclear if gluten is the cause of NCGS or if it might be a reaction to a specific sugar or chemical component found in wheat. For everybody else, eating reasonable amounts of gluten would diversify their diets and help to maintain populations of beneficial bacteria supporting immune system. 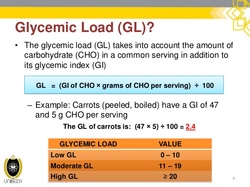 a measure of how quickly a food raises blood glucose levels in average person. glucose index = 100. The glycemic load (GL) of food is a number that estimates how much the food will raise a person's blood glucose level after eating it. Glycemic load is based on the glycemic index (GI), and is calculated by multiplying the grams of available carbohydrate in the food times the food's GI and then dividing by 100. The Glycemic Index (GI) is a scale that ranks carbohydrate-rich foods by how much they raise blood glucose (sugar) levels compared to a standard food - glucose or white bread. 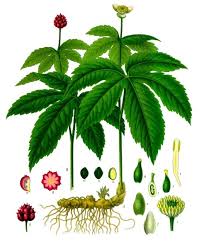 Hydrastis canadensis, perennial herb in the buttercup family with thick, yellow knotted rootstock and purplish hairy stem, hairy leaves, small flowers and berries resembling raspberries. All parts of Goldenseal are supposed to have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, laxative and other medicinal properties. Used in eyewashes and skin lotions, dietary supplements supposed to strengthen immune system and prevent colds. Might have natural contraceptive properties. Should be avoided during pregnancy and lactation, gastrointestinal inflammation, aproinflammatory disorders. High doses my interfere with Vitamin B metabolism. |
Categories
All
|

