126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) and above on more than one testing occasion means that the person has Diabetes.
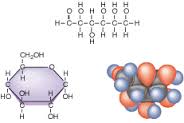
 A simple monosaccharide (sugar) with a molecular formula of C6H12O6. Glucose has several forms. One form is D-glucose, also known as dextrose. The "D" refers to the arrangement of alcohol, or OH, groups on the carbon skeleton of the sugar. L-Glucose could be a low-calorie sweetener, but it does not occur in nature and is too costly to produce. Another form of glucose is beta-D-glucopyranose. As in straight chain D-glucose, the "D" refers to the arrangement of alcohol groups on the carbon skeleton. alpha-D-glucopyranose differs from beta- by the orientation of a single alcohol group around the cyclic carbon backbone. Alpha-D-glucopyranose can be found in solution, or combined with other molecules of sugar. Digestible starch is made of many hundreds of linked alpha-D-glucopyranose units. Glucose is the primary fuel utilized by the brain and working muscles. Blood glucose transported through the bloodstream to supply energy to the body is made from the food we eat or store in the liver and muscle cells. Normal fasting glucose levels are 70 to 99 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L). impaired levels are from 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L). This is called Prediabetes.
126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) and above on more than one testing occasion means that the person has Diabetes.
Comments
|
Categories
All
|