
 Exercises affecting the muscles in the front of the abdomen (belly). also called abdominal or stomach muscles, ab and abs. Abdominal muscles, together with muscles in the back, make up 'core' muscles, supporting the trunk, keeping body stable and balanced, protecting the spine, assisting in the regular breathing movement and keeping abdominal organs such as the intestines in place. These muscles tend to weaken with age unless specifically exercised. Strong back and abdominal muscles can help heal most types of back pain, enhance balance, improve posture, reduce scoliosis symptoms, help prevent falls and injuries during sports or other activities. Causes of abdominal muscle strains include overstretching, overuse or a violent, poorly performed movement of the trunk.
Comments
 something done as an action or a movement, for pleasure, as work (measurable amount of work performed to convert inputs into outputs), or for any other particular purpose. Examples: problem solving, socializing, strength exercise, abdominal exercises, sexual activity 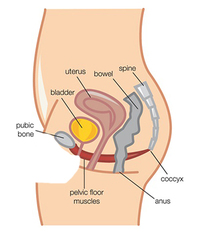 pelvic floor exercises of repeatedly contracting and relaxing the muscles that form part of the pelvic floor (isolated from thigh and buttock muscle contractions). Exercises are usually done to reduce urinary incontinence (for example, in women after childbirth) or reduce premature ejaculatory occurrences and enhance erections in men. Could also help to reduce the feeling of incomplete evacuation in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Exerciser devices include eggs, Ben wa balls (rin-no-tama), vaginal cones, weights, and electrical stimulators and could provide biofeedback devices but are not always recommended. Internet-of-things (IoT) applications include kGoal Smart Kegel Trainer, Skea - exerciser and a video game, Elvie - kegel balls and exercise tracker for pelvic floor and OhMiBod's LoveLife Krush - a "smart" Internet-connected kegel exerciser that doubles as a sex toy. Note potential problems if pushing the device down, mis-training muscles or over-tensing the pelvic floor that can lead to a condition called hypertonicity.  an irresistible urge to perform certain meaningless actions persistently and repeatedly in order to alleviate obsessive fears or intrusive thoughts, in an attempt to make obsessions (frequent upsetting thoughts) go away. For example, if people are obsessed with germs or dirt, they may develop a compulsion to wash their hands over and over again. Other common rituals are a need to repeatedly check things, touch things (especially in a particular sequence), or count things. Healthy people also have rituals, such as checking to see if the stove is off several times before leaving the house. The difference is that people with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) perform their rituals even though doing so interferes with daily life and they find the repetition distressing.  an elevated railway (as in an amusement park) constructed with sharp curves and steep inclines on which cars roll. People with pre-existing conditions could be at risk for injury caused by roller coaster rides. Those with underlying atherosclerosis of blood vessels might be prone to sheer stress and subsequent stroke. The excitement of the ride could release enough adrenalin to trigger both arrhythmia and infarction in susceptible individuals. Subdural hematomas and brain bleeding could happen even without direct trauma as violent movements of the head could tear cortical veins leading to the hematoma. This is rare and is more likely to happen to very young or old people, those taking blood thinners and long term alcoholics. Symptoms of subdural hematoma could be delayed by as much as 2 weeks and include fluctuating levels of consciosness, abnormal movement of the eyes, memory problems, nausea and headache. It can be diagnosed with CT or MRI. Roller coaster could also trigger headaches,vertigo, nausea, short-term memory loss and inflict ear injuries. Ear barotrauma occurs when there is a relatively quick change in pressure between the external environment, the ear drum and the pressure in the middle ear space. Otolaryngologists recommend that passengers remain facing forward for the duration of the ride to not let the full impact of acceleration hit the ear. Hematomas and eye injuries have been documented after one roller coaster ride, yet there are healthy seniors able to tolerate dozens, almost a hundred rides per day. Young teenagers might be most susceptible to motion sickness symptoms, while toddlers are still calibrating their senses and enjoy the lack of predictability. 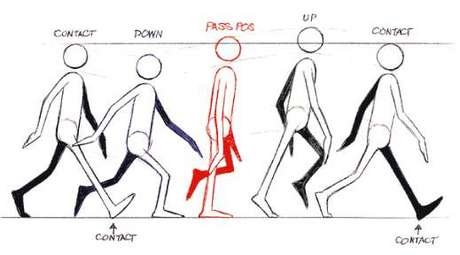 an activity of of traveling by foot in which one always maintains contact with the ground (unlike running) : moving at a regular and fairly slow pace by lifting and setting down each foot in turn, when both feet are never off the ground at once. Regular walking can help ease depression and increase a person's creative output increased by an average of 60%.  Activity involving mental or physical effort to overcome obstacles and achieve a purpose or result. Calories burned range from 1.3 METs per Hr when reading (One MET - metabolic equivalent is defined as 1 kcal/kg/hour and is roughly equivalent to the energy cost of sitting quietly) to 1.8 METs/Hr when taking notes in class, 2.0 METs per hour when working on computer, 3.5 METs/hr when mopping floors, 6.5-8.8 when vigorously shoveling and 9.0 when carrying heavy loads. Examples of most intellectually demanding jobs are air traffic controlling, cryptography, accurate simultaneous interpretation, software engineering, design of complex chip/devices, neurosurgery, mathematics and physics. Music is the most intellectually demanding artform, and motocross is one of the most mentally demanding sports.  moving at a fast pace, with both feet held off the ground at regularly spaced brief intervals. Good cardiovascular (aerobic) exercise. Running speed is affected by stride length (distance between right and left foot contacting the ground), force and frequency as well as total body fitness. Jogging is more loosely defined, the speed is less than 6 mph / 9 km per hr / 2.5 meters per second or 9 mph / 14 km per h / 4 m per sec for athletes. At speeds up to 2m/s (7 mph), walking requires less energy than running. As speed increases, different strides of running become more economical.  being in a position in which one's weight is supported by one's buttocks rather than one's feet when back is upright, especially when engaged in a particular activity. 1 Metabolic Equivalent of Task (MET), a physiological measure expressing the energy cost of physical activities, is defined as the rate of energy produced per unit surface area of an average person seated at rest. Here are sample METs per activities involving sitting: Sitting, playing with animals. light, only active periods 2.5 Sitting quietly, smoking. listening to music (not talking or reading), watching a movie in a theater 1.0 Sitting and reading 1.3 Sitting and eating 1.5 Sitting-arts and crafts, light effort 1.5 Sitting-arts and crafts, moderate effort 2.0 Sitting at a sporting event, spectator 1.5 Sitting while taking medication 1.0 Sitting while having hair or nails done by someone else 1.0  physical exercises enhancing or maintaining physical fitness performed to strengthen the muscles, by isolating specific muscles to produce optimal workout results. Help protect joints, muscles, and tendons from strains and tears, prevent osteoporosis (the loss of bone density) and fractures. Strength training can also improve balance and help prevent fat gain, increase the efficiency of oxygen use by muscles, reduce arterial aging, and improve immune function, thus decreasing the risk of early onset of chronic diseases such as arthritis. The disadvantage is potentially disproportionate growth of specific muscles within a muscle group. |
Categories
All
|
