
 Cravings for fatty or oily foods. Could imply cravings for flavors, nutrients missing in diet, mineral deficiencies (Magnesium) or slow metabolism and elevated levels of chemicals in tissues (like Copper or Calcium), or psychological cravings.
Comments
 complex type of odor resembling that of the waste matter discharged from the bowels, influenced by dietary and endogenous contributions. Major components are sulfurous (hydrogen sulfide: odor of rotten eggs, butyl mercaptan: skunk, methyl mercaptan: rotting cabbage, sweaty feet), nitrogen, phosphorous and heterocyclic organic compounds such as indole (napthalenelike "mothball" odor) and scatole (3-methylindole produced from tryptophan in the digestive tract, classical "fecal odor"), ammonia and trimethylamine. Fatty acids contributing to smell include Acetic and Propionic acids (vinegar), Butyric acid (rancid butter), and Valeric acid (cheesy and sweaty). These chemicals occur as part of the normal digestive processes in all mammals. The diet, and the configuration of digestive system determine the types and amounts of the very large number of possible odoriferous substances in feces, and so are diseases and conditions. Obese individuals, for example, have more ester compounds, hydrogen sulfide is increased in Ulcerative Colitis, and fruity-alcoholic-fermented-smelling aldehydes are increased in Celiac disease. Colorectal cancer patients have higher levels p-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (woody odor), IBS with diarrhea increases esters of short chain fatty acids and cyclohexanecarboxylic acid (fruity and cheesy). Fecal breath odor can indicate certain types of intestinal blockage.  Experiencing a desire or need for food. Ghrelin, a hormone produced by the stomach, is a hunger stimulant and so is the deficit of cholecystokinin (CCK). Other factors are blood levels of glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids and neural signals from GI tract. Craving food does not necessarily mean an energy deficit. It could be instead fueled by the anticipated pleasure of eating.  feeling that a bowel movement has not been as complete as it should be. Could be because of small stools or continued urges after repeated bowel movements, due to visceral hypersensitivity in the large intestine and motility dysfunction, or the fact that the muscles of the large intestine do not operate smoothly, so the person can't pass well-formed stools.  State of mental or emotional strain or suspense capable of affecting physical health, usually characterized by increased heart rate, a rise in blood pressure, muscular tension, irritability, and depression. Many stressors (stressful circumstances) are not inherently stressful. Conscious and unconscious responses of our inner world that determine whether it will make us actually feeling stressed. Studies suggest that up to 75-90% of all health problems are related to stress.  feeling a need or desire to drink, feeling dehydrated. Could be the reaction to eating salty foods and not drinking enough water or fluid loss during exercise, fever, heat exposure, diarrhea, vomiting, injuries to skin, increased urination due to infection, dry mouth syndrome. There is often this feeling of needing to drink during and after anxiety attacks. Excessive thirst may also be a symptom of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) and diabetes.  seeds of Fenugreek used as spice (especially ground flavoring and in curry powder) and a supplement. It is a rich reservoir of medicinal properties that imparts many health benefits. It reduces the risk of heart disease, lowers blood cholesterol, increases levels of potassium, controls blood sugar, aids digestion, reduces heartburn, helps reduce menstrual discomfort (one of its compounds, diosgenin, has properties similar to estrogen, used for erectile dysfunction and libido.  a white- or blue-flowered herbaceous plant of the pea family (Trigonella foenum-graecum), used as an herb (dried or fresh leaves), spice (seeds), vegetable (fresh leaves, sprouts, and micro-greens) and an herbal supplement. It has a distinctive sweet and slightly nutty aroma. Both the leaves and seeds of fenugreek can be used in the treatment of anemia (increases iron) or diabetes (reduces sugar). Fenugreek leaves are used for treating kidney stones. Seeds can be used to counter heartbutrn/acid reflux and for suppressing appetite. Water boiled with fenugreek seeds or a paste of fresh fenugreek leaves can be used as a face mask to help prevent blackheads, pimples, and wrinkles. 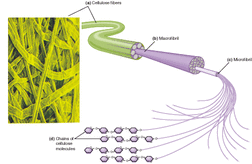
Indigestible portion of plant foods.
Fiber can be broadly separated into insoluble and soluble types, based on their ability to dissolve in and retain water and fermentation in colon (soluble) or intestine (insoluble). Soluble fiber include fructans (inulin and galactooligosaccharies, see FODMAPs), polyuronide compounds (pectins, aliginates, natriumalginat, carrageen). Insoluble fiber includes lignins, cellulose, chitin and resistant starch. All types of soluble fibers slow digestion, flush fatty acids out of the body and help to lower bad (LDL) cholesterol. Insoluble fibers help hydrate and move waste through intestines. 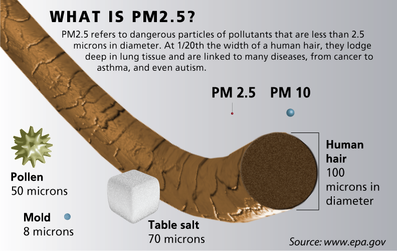 Particles less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter (PM2.5) are referred to as soot or "fine" particles and are believed to pose the greatest health risks. 1/20th the width of a human hair, these tiny particles can lodge deep in the lung tissue and impair breathing capacity. They are linked to many diseases, including cancer, asthma and autism. As many as 64,000 premature deaths occur each year from cardiopulmonary causes attributable to particulate air pollution, according to the estimates of Natural Resource Defence Counsil. Most particulate emissions result from burning fossil fuels -- coal, oil, diesel, gasoline -- or wood. Old coal-fired power plants, industrial boilers, diesel and gas-powered vehicles and wood stoves are some of the worst culprits. High-temperature industrial processes such as metal smelting and steel production are also significant sources. Everyone can help cut down on particulate matter pollution by conserving energy and choosing cleaner, more efficient energy sources for home heating and cooling, transportation, and appliances. Read more about other types of particles in the air, including PM10. |
Categories
All
|
