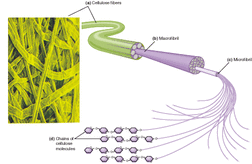
Fiber can be broadly separated into insoluble and soluble types, based on their ability to dissolve in and retain water and fermentation in colon (soluble) or intestine (insoluble). Soluble fiber include fructans (inulin and galactooligosaccharies, see FODMAPs), polyuronide compounds (pectins, aliginates, natriumalginat, carrageen). Insoluble fiber includes lignins, cellulose, chitin and resistant starch.
All types of soluble fibers slow digestion, flush fatty acids out of the body and help to lower bad (LDL) cholesterol. Insoluble fibers help hydrate and move waste through intestines.

