
 type of yogurt that has more protein and a thicker, creamier consistency because of an additional straining step. It also has less carbohydrates, unless sweetened. Main probiotic cultures in Chobani yogurt are Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, and Bifidus. This can, however, vary - recalled Chobani yogurt, for example, contained mold Mucor circinelloides and a large number of Oceanospirillales.
Comments
 A thick paste of mashed avocado, often combined with limes/citrus juice, onion, tomatillos/tomatoes, chilli peppers and seasonings and usually served as a dip or in salads. Rich in fiber, potassium and other essential nutrients, guacamole can promote health and prevent certain illnesses when included in a healthy diet. Poor refrigeration may make guacamole prone to contamination that can cause foodborne illness such as listeria. The number of reported foodborne disease outbreaks attributable to salsa or guacamole increased in the United States from 1984 to 2008, especially in later years, and especially in restaurants. 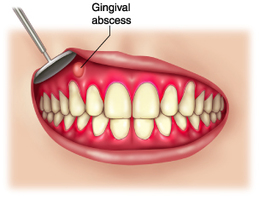 area of pus that forms as part of the body's effort to fight a bacterial infection. Could be accompanied by persistent, throbbing pain, sensitivity to heat, pressure while chewing, even fever and swollen lymph nodes. The immune system sends white blood cells to the area to try to get rid of the bacteria. Pus contains both live and dead cells. It also contains enzymes. An abscess forms when there is no way for pus to drain. Dental or dentoalveolar abscess is a denomination used to describe localized collection of pus in the alveolar bone at the root apex of the tooth. It usually occurs secondary to dental caries, trauma, deep fillings or failed root canal treatment. Once the intact pulp chamber is breached, colonization of the root canals occurs with a diverse mix of bacteriological agents. The pathogenesis of dentoalveolar abscess is polymicrobial in nature, comprising of various facultative anaerobes, such as the viridans group streptococci and the Streptococcus anginosus group, and strict anaerobes, especially anaerobic cocci, Prevotella and Fusobacterium species. If the abscess ruptures, a sudden rush of foul-smelling and foul-tasting fluid will spill into the mouth. In the mouth, abscesses form in the gums, teeth or roots of teeth. Bacteria can enter and cause an abscess in several ways:
without burning your mouth,and rinse for two minutes every four hours, this will provide you relief. Avoid eating, hot, spicy and hard food. Don't brush hard or chew hard foods from that area. Healing compresses with wet tea bags could be also helpful with dental abscesses. Either black tea, green tea, or Echinacea tea would work. Simply soak it in warm water, place on the swollen area, then hold it. After pus is released, rinse with salt water, hydrogen peroxide solution, or other disinfectant. Even if these remedies seem to help, but your abscess is continually draining, you need to see your dentist as soon as possible. Good oral hygiene can help prevent abscesses. This means that you need to keep teeth and gums free of food.  a soft cohesive preparation (usually made of sweetened chicle) for chewing but not swallowing Chewing gum could temporarily improve cognitive abilities, prevent cavities, help recover from surgery, and is used as a novel approach for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).  Various species of microbes represented in our gastrointestinal tract, also known as gut flora or microbiota. Microbiome often refers to the combined genetic material of these species, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, protists and viruses. Internal microbial communities are responsible for appetite, behavior, consuming and digesting foodstuffs. Gut microbiome is responsible for about 70% of the total immune response and 90% of the serotonin production in the body. 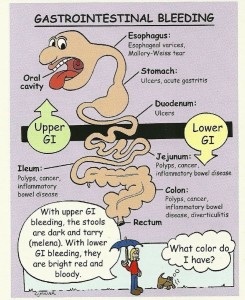 Bleeding from any part of the gastrointestinal tract including esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), rectum and anus. This symptom can be a life-threatening emergency. GI bleeding first appears as blood in vomit or stool, black or tarry stools. It can be suspected if the person experiences abdominal pain, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, anemia. GI bleeding can be diagnosed by lab tests and procedures such as endoscopic procedures: esophagogastroduedonoscopy (EGD), gastroscopy, endoscopic ultrasound, sigmoidoscopy, or colonoscopy. The causes of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding are classified into upper or lower, depending on their location in the GI tract. Treatment depends on the cause or location of the bleeding and includes:
 a hot fragrant spice made from the rhizome of a plant (Zingiber officinale) of tropical southeast Asia having yellowish-green flowers and a pungent aromatic rhizome. The tuber is consumed whole as a delicacy, medicine, or spice. It is chopped or powdered for cooking, preserved in syrup, or candied. The primary known phytochemicals, biophenols and other compounds of ginger root include gingerols, zingibain, bisabolene, oleoresins, starch, essential oil (zingiberene, zingiberole, camphene, Cineole, borneol), mucilage, and protein.  Healthy skin appearance. Skin is the outermost tissue of the body with an area of approximately 16, 000 cm2 for an adult and represents about 8% of the body weight. It has a very complex structure that consists of many components. Cells, fibers and other components make up several different layers that give skin a multi-layered structure. Veins, capillaries and nerves form vast networks inside this structure. In addition, hairs stick out from the inside of skin. Numerous fine hair furrows are scattered over the surface of skin. Except for a few specific localized areas, human skin normally ranges from pH 4.2–6.0 due to the abundance of fatty acids that are present. Skin should be slightly acidic - women with an alkaline stratum corneum (the skin's outermost layer) develop more fine lines and crow's-feet—and are more prone to sun damage—than those with acidic skin. On the other hand, excess fat could attract microbes causing acne.  an adhesive, derived from natural and plant sources, used for sticking objects or materials together. About 40 lb of glue are used per year for every person in America including furniture, plumbing, shoes, books, buildings, and automobiles - all this items use glue in some part of their construction. Three main classes of glues are bone glue, hide or skin glue, and fish glue. Technically, gums and cements are not glues, but adhesives, as they are made from synthetic materials, but consumers tend to also call them glue. Collagenous animal parts such as bones, hides, horns and hooves can be turned into hard gelatin and then "diluted" into glue. Starch-based glue, better known as paste, is made from carbohydrates extracted from plants. Mucilage is a polysaccharide extracted from plant roots and seeds. Epoxy is made from a class of synthetic thermosetting polymers containing epoxide groups. A “glue” produced by mussels to help them stick to rocks underwater has been used to develop a new type of adhesive to perform repairs during surgery. Incorporating silver into the glue-like material can make it antibacterial. Research shows that some glue chemicals affect cognitive abilities of the brain even 30 years after exposure (original study). |
Categories
All
|
