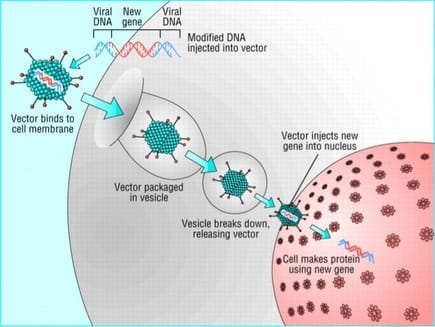
DNAi is inserted, deleted or replaced using "molecular scissors" - engineered nucleases creating site-specific double-strand breaks at desired locations in the genome. These breaks are further edited and repaired through nonhomologous end-joining or homologous recombination.
There are currently four families of engineered nucleases being used: meganucleases, zinc finger nucleases, transcription activator-like effector-based nucleases, and the CRISPR-Cas system.
