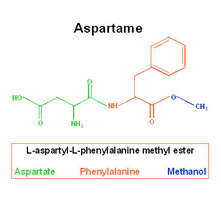
Aspartame is roughly 200 times sweeter than sucrose and is fully digested by the body, breaking down to methanol, formaldehyde, formic acid, phenylalanine and aspartic acid. In carbonated drinks, it also creates a substance called aspartylphenylalanine diketopiperazine. US FDA has set the ADI for aspartame at 50 mg/kg of body weight/day. In contrast, the European Commission’s Scientific Committee on Food (SCF) has set it at 40 mg/kg. This means that an adult should not consume more than 20 aspartame-sweetened 12oz carbonated soft drinks per day.
