
The cheese is made by inoculating warmed milk with mesophilic bacteria, then adding rennet and allowing the mixture to coagulate.
At the beginning of its ripening (48 hours), Camembert is crumbly and soft and gets creamier over time (usually 2-3 weeks). A genuine Camembert has a delicate salty taste.
Consumption of Camembert cheese increases Lactococcus lactis and Leuconostoc mesenteroides levels in the gut.
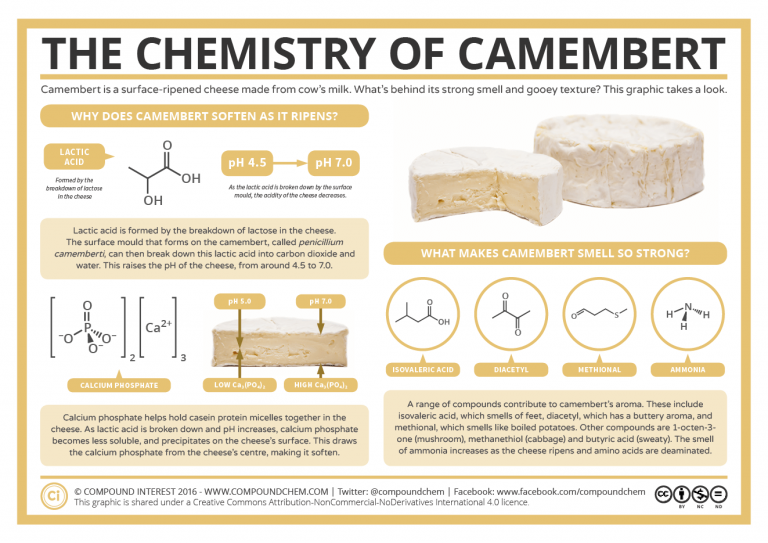
smell? This is contributed to by a wide range of compounds, many of which are produced as a consequence of the ripening process. They include such delights as isovaleric acid, which in isolation smells of cheesy feet, diacetyl (buttery), methanethiol (cabbage-like), methanol (boiled potatoes), 1-octen-3-one (mushroom-like), and butyric acid (sweaty). Of course, though some of these sound pretty unpleasant in isolation, they come together to contribute the characteristic camembert smell.
Another compound that can make a significant contribution to camembert’s aroma is ammonia. This is produced by the deamination of amino acids on the cheese’s surface. The amount of ammonia increases as the cheese ripens; after a significant amount of time, the smell can become very strong, at which point the cheese is probably past its best!
