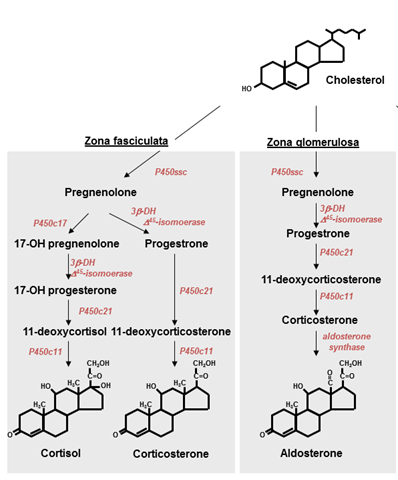
There are two kinds of corticosteroids: glucocorticoids (such as prednisone, beclomethasone, dexamethasone, cortisone, cortisol and hydrocortisone) and mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone and fludrocortisone). Glucocorticoids are involved in glucose metabolism, mineralocorticoids control salt and water balance.
Corticosteroid drugs, also known as cortisone-like medicines and steroids are available in different forms, including: tablets (oral steroids), injections (into blood vessels, joints or muscles), inhalers (mouth or nasal sprays) and lotions, gels or creams (topical steroids).
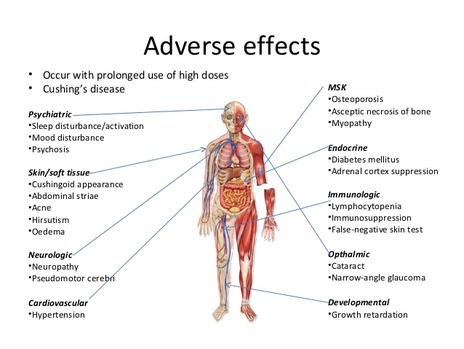
Topical corticosteroids have been ranked in terms of potency into four groups consisting of seven classes. Class I topical corticosteroids are the most potent (e.g. Clobetasol propionate) and Class VII are the least potent (e.g. Hydrocortisone acetate). Over-the-counter drug Flonase (Fluticasone Propionate Nasal Spray) is relatively potent and in cream form is classified as group V. Fluticasone propionate was 3-fold to 5-fold more potent than dexamethason in one in-vitro assay. Efficacy and side-effects are greatest with the Class I ultra-high-potency preparations which should only be used for limited time periods. Efficacy and side-effects are greatest with the Class I ultra-high-potency preparations which should only be used for limited time periods (2-3 weeks).
