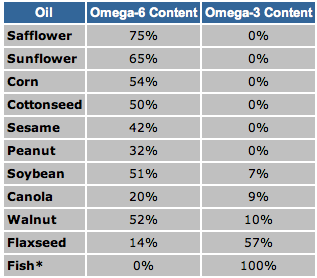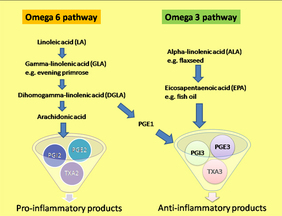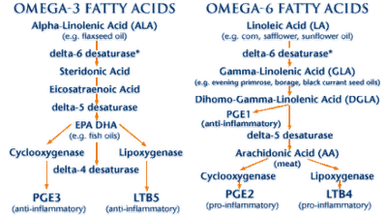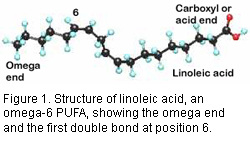
There are several different types of omega-6 fatty acids, some of them promote inflammation but others fight it. Most omega-6 fatty acids in the diet come from vegetable oils, such as linoleic acid (LA, different from alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is an omega-3 fatty acid(. Linoleic acid is converted to gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) in the body. It can then break down further to arachidonic acid (AA). GLA is found in several plant-based oils, including evening primrose oil (EPO), borage oil, and black currant seed oil. Omega-6 fatty acids are available in supplemental oils that contain linoleic acid (LA) and GLA, such as EPO (Oenothera biennis) and black currant (Ribes nigrum) oils. Spirulina (often called blue-green algae) also contains GLA.