
Considered dark meat as it is darker than leaner breasts because leg muscles are used more and hence have more myoglobin proteins, which help ship oxygen to muscle cells and are highly pigmented.
When red or dark meat is cooked, the myoglobin's color changes depending on what the meat's interior temperature is. Above 140° F (60° C), myoglobin loses its ability to bind oxygen, the iron atom at the center of its molecular structure loses an electron, and a tan-colored compound called hemichrome is formed, giving medium-done meat its color. When the interior of the meat reaches 170° F, hemichrome levels rise, and the myoglobin becomes metmyoglobin, which gives well-done meat its brown-gray shade.
When cooking turkey: above 145°F, white meat begins to dry out. Dark meat, with its connective tissue, on the other hand, has to be cooked to at least 165°F
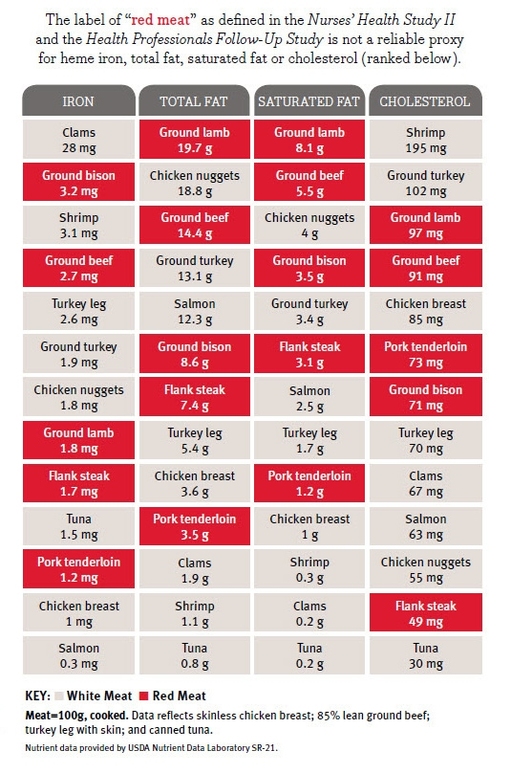
Virtually all dietary studies categorize poultry as "white meat" and "dark meat", while four-legged land animals such as beef, pork and lamb are considered "red meat." Yet in culinary or cultural contexts, veal is often considered a white meat and duck or goose may be classified as red. Food scientists point to higher concentration of myglobin and slow-twitch muscle fibers as the primary determinant of red meat; however, the dark meat of chicken or turkey usually has more myoglobin than veal or pork.
