
Cinnamon spice creates sensation of warmth and is linked to creativity and willingness to spend more money.
 aromatic spice made from the dried bark of Cinnamomum, a Southeast Asian tree. The most important Cinnamomum oils in world trade are those from C. verum (cinnamon bark and leaf oils), C. cassia (cassia oil) and C. camphora (sassafras and Ho leaf oils). Cinnamon spice creates sensation of warmth and is linked to creativity and willingness to spend more money.
Comments
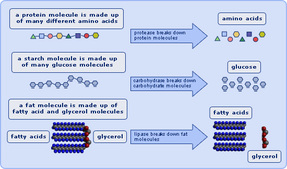 Enzymes that break down proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and fat molecules into smaller parts, in order to facilitate their absorption by the body. They can be found in the saliva, stomach the pancreatic juice, and in the intestinal (small and large) secretions, or as part of the lining of the gastrointestinal tract. Digestive enzymes include:
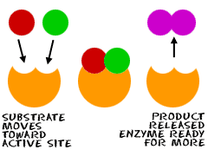 biological molecules, mainly proteins, that catalyze (accelerate, increase the rates of) chemical reactions. Metabolic enzymes assist in a wide range of basic bodily processes, from breathing to thinking. One example of an enzyme is cytochrome, which aids the respiratory system by catalyzing the combination of oxygen with hydrogen within the cells. Cytochrome b is a part of complex III that helps to create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy source in mitochondria. Mutations in the MT-CYB (mitochondrially encoded cytochrome b) gene can cause muscle weakness (myopathy) and pain, especially during exercise (exercise intolerance). More severely affected individuals can have problems with other body systems, including the liver, kidneys, heart, and brain. Other enzymes are involved in digestion. Some of them come from raw foods and include proteases, digesting proteins; lipases, digesting lipids or fats; and amylases, helping to digest carbohydrates. Human digestive glands also secrete enzymes that break down nutrients - like amylase in the saliva and pepsin helping to digest protein in the stomach. 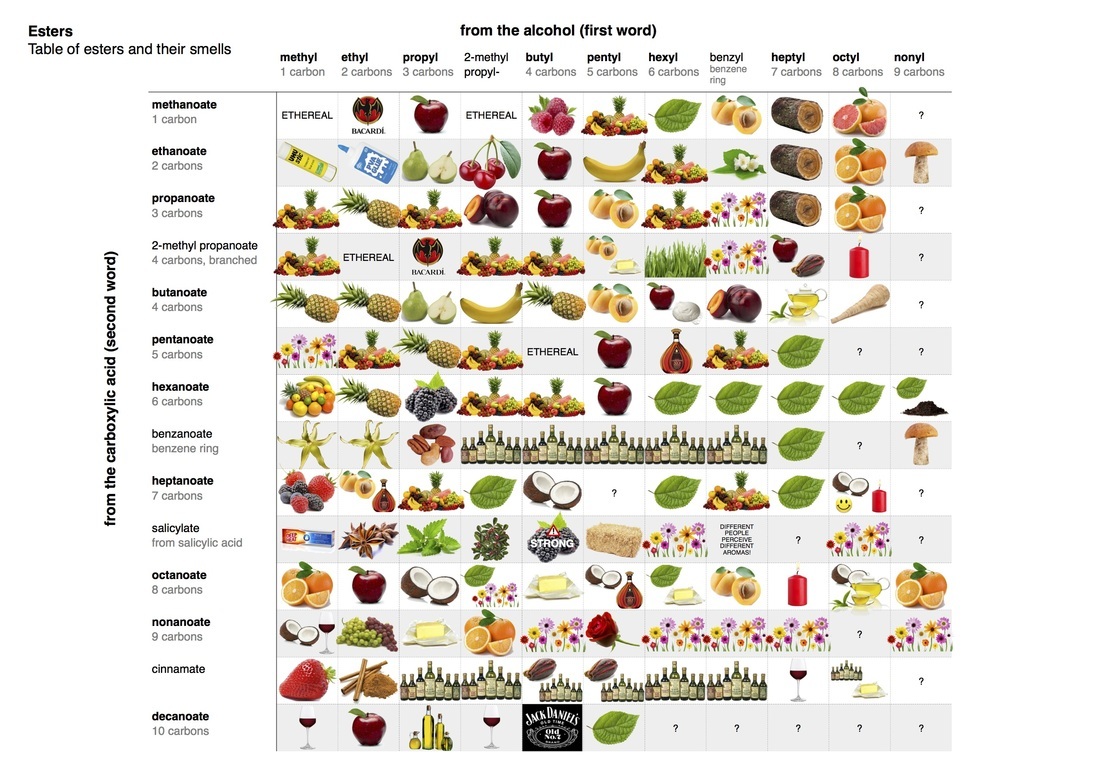 organic compounds made by replacing the hydrogen of an acid by an alkyl or other organic group. Many naturally occurring fats and essential oils are esters of fatty acids. Analysis of esters in urine, breath and other human fluids could aid in medical diagnostics. For example, carnitine and glycine esters in urine are associated with organic acidopathies, while certain esters in breath could indicate exposure to phthalates. 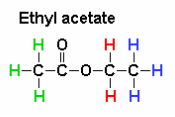 organic compound, ester of ethanol and acetic acid, carboxylic ester. It is produced by Acetobacter, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Baker's yeast) & other microbes, by Anthemis nobilis (Roman chamomile) and Rubus species (raspberries, blackberries). It is used as a plastics solvent and in flavorings, artificial fruit essences, confectionery and perfumes. It evaporates at a fast rate, leaving but the scent of the perfume on the skin. Ethyl acetate is also used as a solvent in the manufacture of modified hop extract and decaffeinated tea or coffee, for color inks to mark fruit or vegetables and as insecticide (asphyxiant) in the field of entomology. Ethyl acetate contributes to the notorious “nail polish remover” scent in wine and human body odor. It is also responsible for apple-like, banana-like, raspberry-like and strawberry aromas. Ethyl acetate is also found in cereal crops, radishes, fruit juices, beer,and other spirits. Short-term exposure to high levels of ethyl acetate results first in irritation of the eyes, nose and throat, followed by headache, nausea, vomiting, sleepiness, and unconsciousness. High concentrations can cause CNS depression and congestion of the liver and kidneys. Very high levels may cause a stupor but it is relatively non-toxic. Chronic poisoning has been described as producing anemia, leucocytosis (transient increase in the white blood cell count), and, clouding of the eye, damage to the lungs and heart and kidney and liver problems, cloudy swelling, and fatty degeneration. Athletes exposed to relatively lower levels of Ethyl acetate in facilities where they exercise experience wheezing coughing, rhinitis, or shortness of breath. Ethyl acetate has been shown to exhibit anti-arthritic, anti-mycotic, anti-nociceptive, hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory functions (PMID 12673020 , 12781815 , 21340514 , 17507320 ,20363280). Ethyl acetate belongs to the family of Carboxylic Acid Esters. These are carboxylic acid derivatives in which the carbo atom from the carbonyl group is atached to an alkyl or oaryl moiety through an oxygen atom (forming an ester group). Ethyl acetate can be found in human biofluids such as feces, saliva and urine. It is present in small amounts in healthy children and adults. Abnormal concentrations can be found in Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), Celiac disease and breast cancer. 
Indigestible portion of plant foods.
Fiber can be broadly separated into insoluble and soluble types, based on their ability to dissolve in and retain water and fermentation in colon (soluble) or intestine (insoluble). Soluble fiber include fructans (inulin and galactooligosaccharies, see FODMAPs), polyuronide compounds (pectins, aliginates, natriumalginat, carrageen). Insoluble fiber includes lignins, cellulose, chitin and resistant starch. All types of soluble fibers slow digestion, flush fatty acids out of the body and help to lower bad (LDL) cholesterol. Insoluble fibers help hydrate and move waste through intestines. 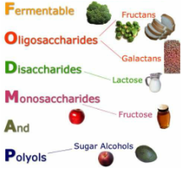
Fermentable Oligo-, Di- and Mono-saccharides and polyhydric alcohols poorly absorbed in the small intestine. Include Fructose, Lactose, Fructan & otherFructooligosacharides, Galactooligosaccharides and Polyols.
FODMAPs contribute to "Functional gut" symptoms (bloating, wind, abdominal distension, discomfort, pain, altered bowel habits). With Fructose intolerance, symptoms peak after about 90 mins, with inulin sensitivity, symptoms peak after about 4 hours of eating. Low FODMAP diet has been shown to help sufferers of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), Irritable Bowel Disease (IBD: Crohn's, ulcerative colitis), celiac disease, fructose malabsorption, and patients with colectomy. High FODMAP foods include apples, apricots, asparagus, beans, cashews, dates, garlic, milk, onions, peaches, pears, pistachios, plums, rye, wheat. 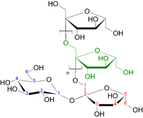 polymers of fructose naturally produced by 15% of flowering plant species, consist of inulin (prebiotic), inulo-n-oses, and other selected vegetable fibers. Some species such as artichoke (Cynara scolymus) and globe thistle (Echinops ritro) store fructans with a considerably higher degree of polymerization than the one observed in chicory (Cichorium intybus) and Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus). Fructans are a type of FODMAPs. 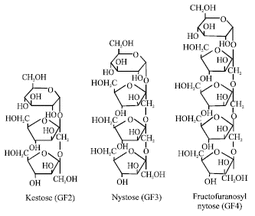 Fructooligosaccharide (FOS), also called oligofructose or oligofructan, is a class of oligosaccharides used as alternative sweeteners and as prebiotics. They occur naturally in plants that occur naturally in plants such as onions, chicory, garlic, asparagus, wheat, banana, artichoke, tomatoes and other fruits, vegetables and grains. They also can be derived from cane sugar. Fructooligosacharides are short-chained fructans, a type of FODMAPs |
Categories
All
|